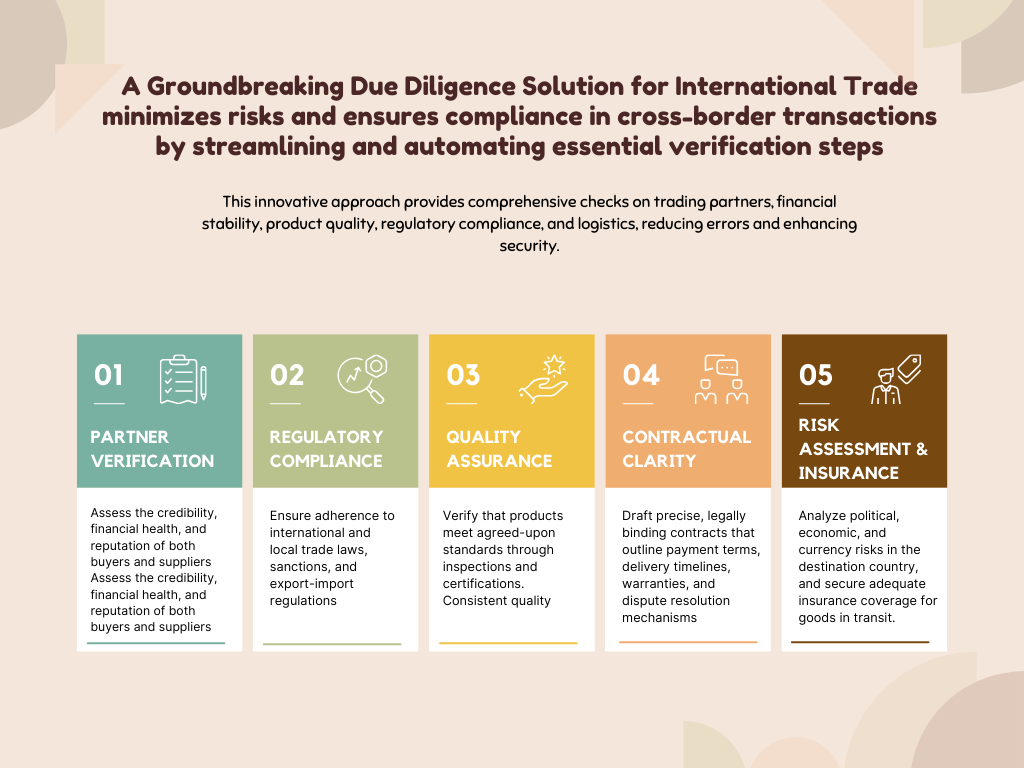
The One Stop Solution
B2B Services
Fastrider’s Fraud Detection system is designed to protect the integrity of its supply chain operations by identifying and mitigating risks from fraudulent activities.
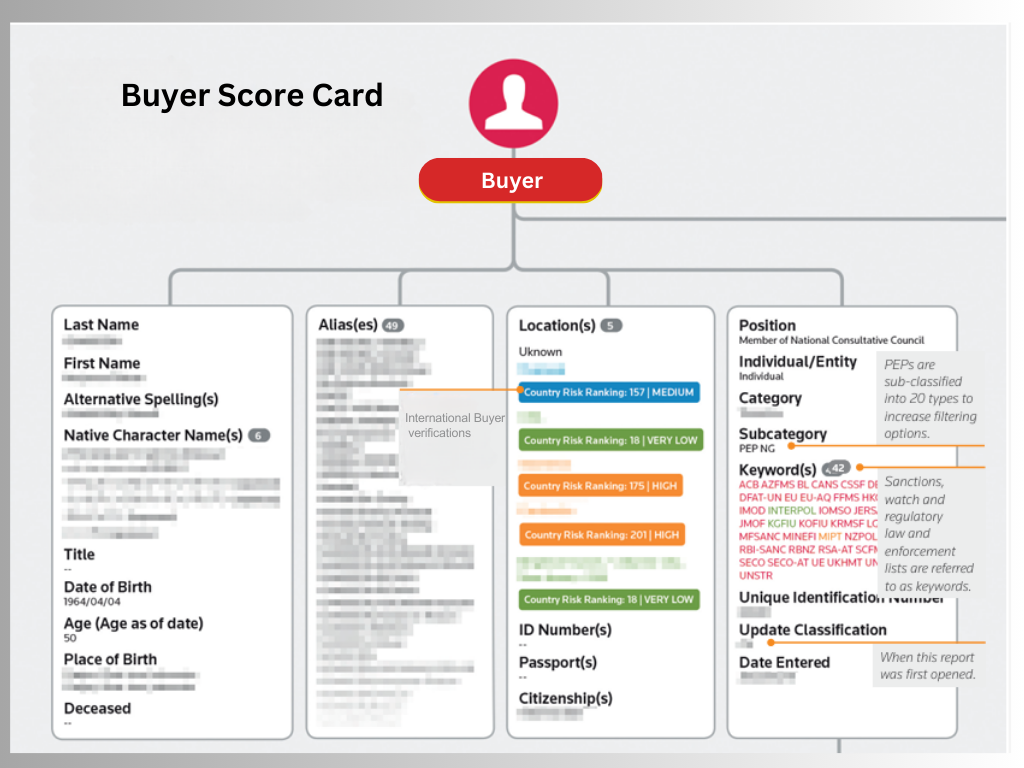
Buyer and Supplier Verification
Validate the legal status, financial stability, and reputation of the trading partner
Financial Due Diligence
Assess creditworthiness, payment history, and any outstanding debts
Compliance and Regulatory Checks
Compliance and Regulatory Checks for Vendor Compliance are essential to ensure that vendors adhere to legal, industry, and ethical standards, safeguarding against potential risks and liabilities. Key aspects include
Product and Quality Verification
Confirm product specifications, standards, certifications, and quality control requirements
Contractual Due Diligence
Draft clear contracts outlining terms and conditions, including payment, delivery, warranty, and dispute resolution.
Logistics and Transportation Due Diligence
Assess shipping routes, freight forwarders, and logistics providers to avoid delays or losses.
Currency and Payment Terms
Consider currency risks and fluctuations, and use hedging strategies if necessary.
Taxation and Tariff Analysis
Review applicable taxes, tariffs, and duties in the destination country to avoid unexpected costs.
Environmental and Social Due Diligencets
Ensure compliance with environmental laws, waste management, and pollution controls.
Political and Economic Risk Assessment
Review the political stability, economic conditions, and risk of conflict in the destination country.
Sanctions and Embargo Checks
Ensure that trade partners are not on sanctions lists (e.g., OFAC, UN, EU lists) and comply with any embargoes..
Cultural and Language Considerations
Understand cultural norms, negotiation styles, and communication preferences to foster better relationships.
Buyer and Supplier Verification
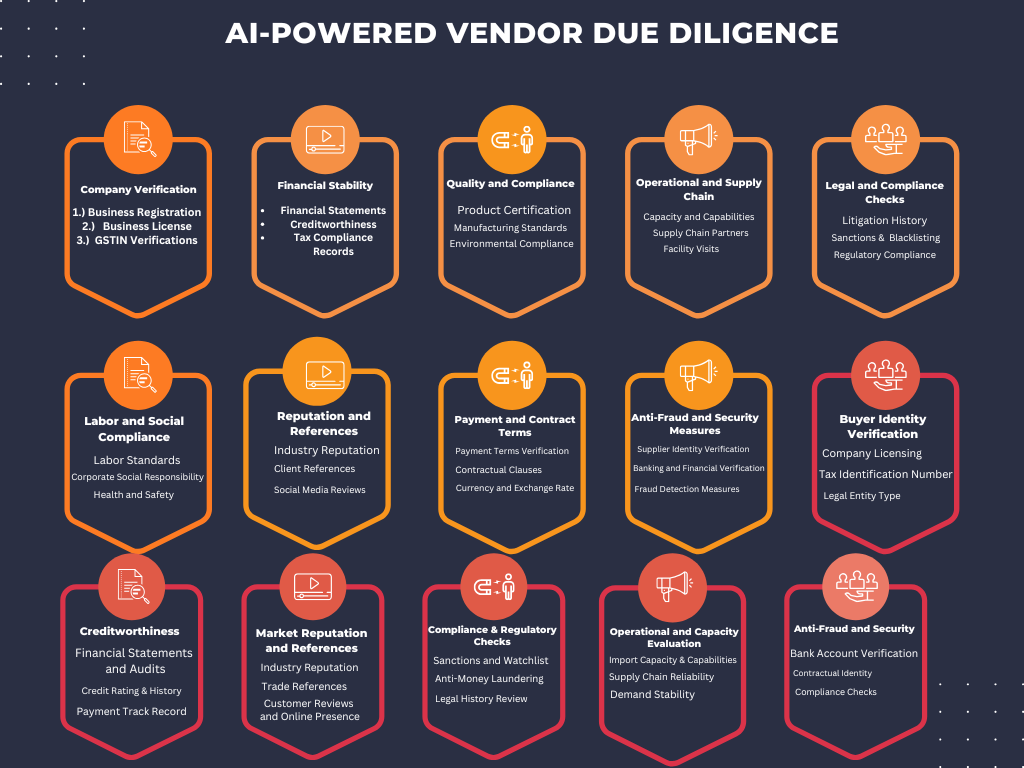
Buyer and Supplier Verification is a key aspect of vendor due diligence, ensuring partners in international trade meet legal, financial, and operational standards. This process includes
Financial Due Diligence for Buyer and Suppliers


Financial Due Diligence for Buyers and Suppliers is essential in assessing the financial reliability and stability of trade partners, helping to prevent financial risks and ensure smooth transactions. Key aspects include.
- Creditworthiness Assessment
- Payment History Analysis
- Financial Statement Review
- Debt and Liability Check
- Sample Request Fees
- Scams Involving Shipping and Handling Fees
Compliance and Regulatory Checks
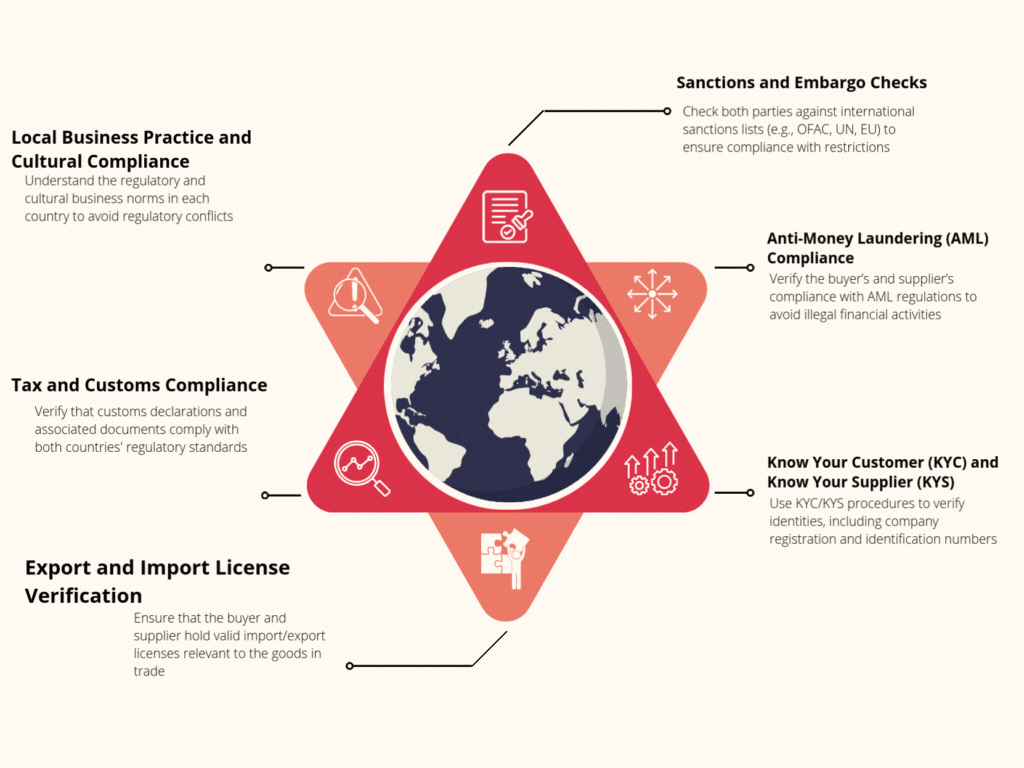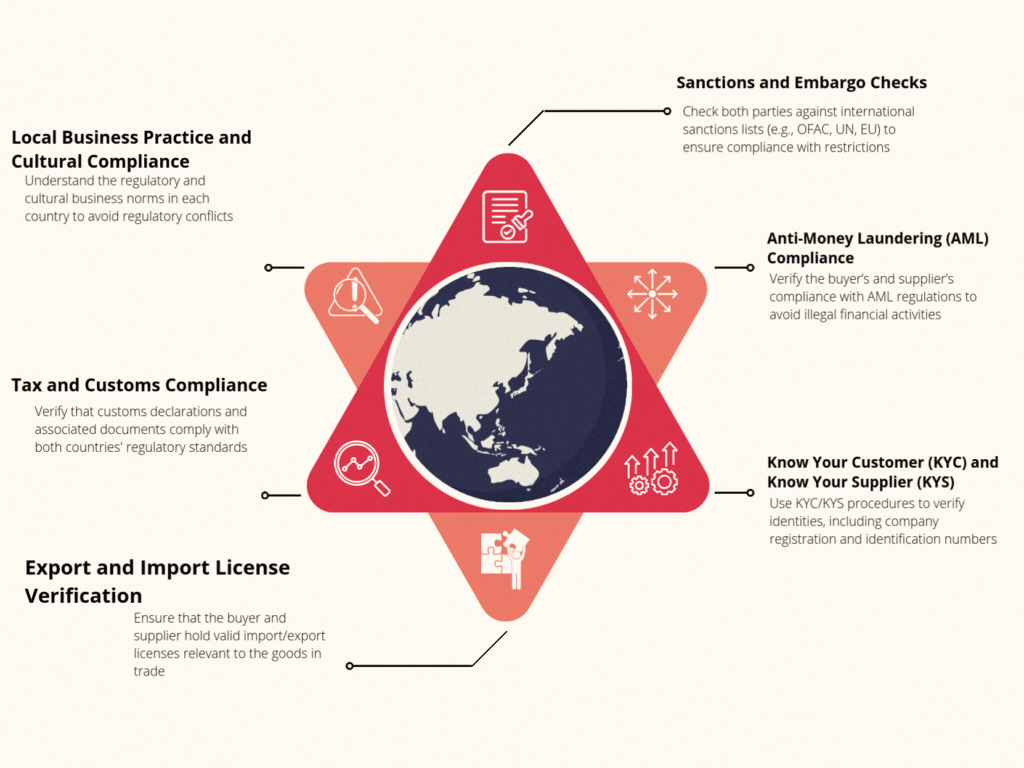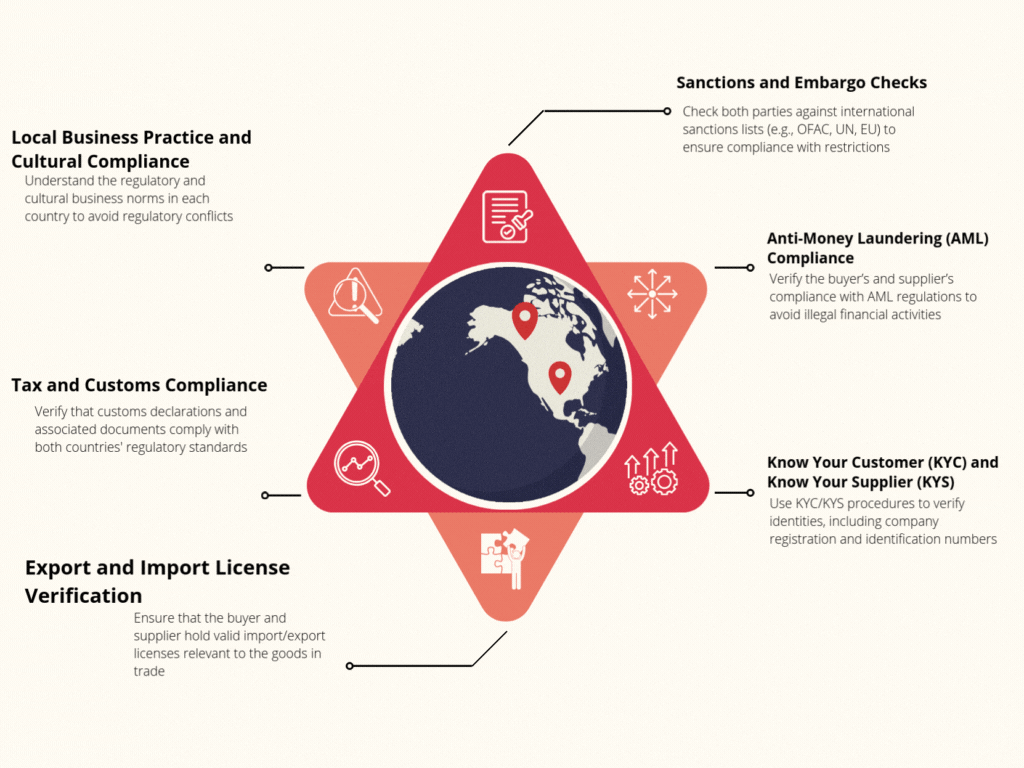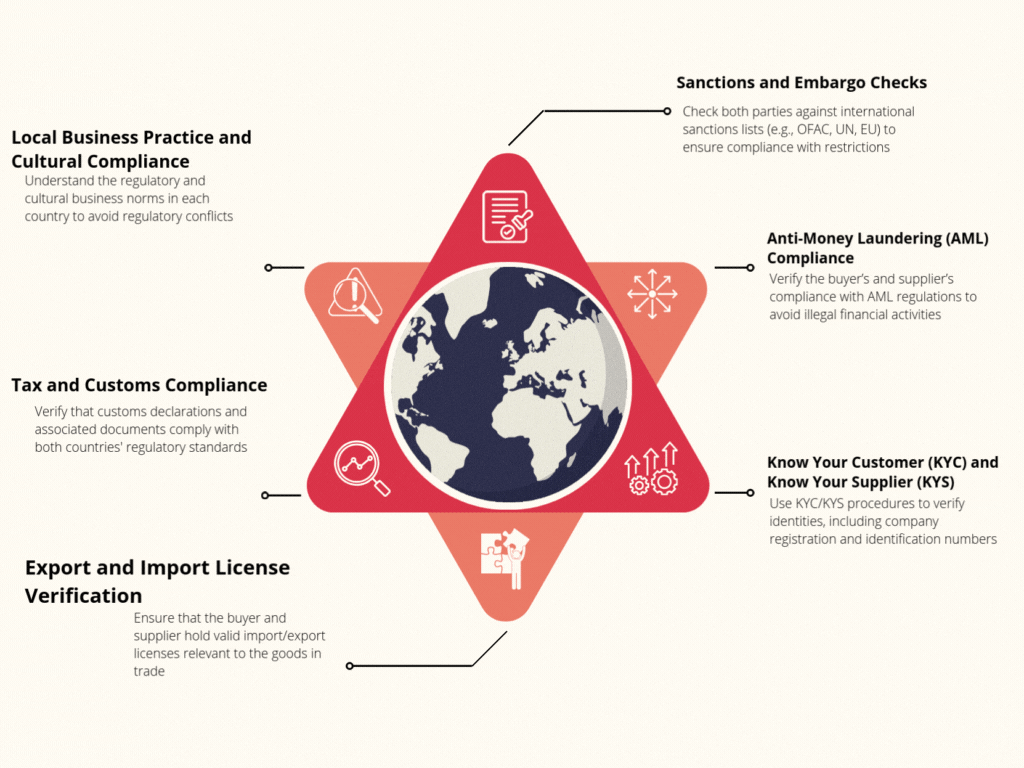
Compliance and Regulatory Checks for Vendor Compliance are essential to ensure that vendors adhere to legal, industry, and ethical standards, safeguarding against potential risks and liabilities. Key aspects include
Know About Us- Anti-Corruption and AML Compliance
- Sanctions Screening
- Labor and Environmental Standards
- Data Privacy and Cybersecurity Compliance
- Export-Import Regulations
Product and Quality Verification
Product and Quality Verification is a vital part of the buyer and supplier verification process, ensuring that products meet the agreed-upon standards before they reach the market. This process helps in maintaining quality consistency, meeting regulatory requirements, and protecting brand reputation.
- Product Specifications Review
- Quality Certification Verification
- Sampling and Testing
- Third-Party Inspection
- Compliance with Local Regulations
- Packaging and Labeling Verification
- Supplier Quality Management Systems
- Warranty and After-Sales Support Agreements
Contractual Due Diligence
Contractual Due Diligence is essential in the buyer and supplier verification process to ensure that agreements protect both parties' interests, reduce risks, and provide clarity on roles and obligations.
- Clear Payment Terms
- Delivery and Incoterms Specification
- Product Quality and Standards Clauses
- Dispute Resolution Mechanism
- Termination and Exit Clauses
- Confidentiality and Intellectual Property (IP) Protection
- Compliance with Local and International Regulations
- Warranty and Liability Provisions
Logistics and Transportation Due Diligence
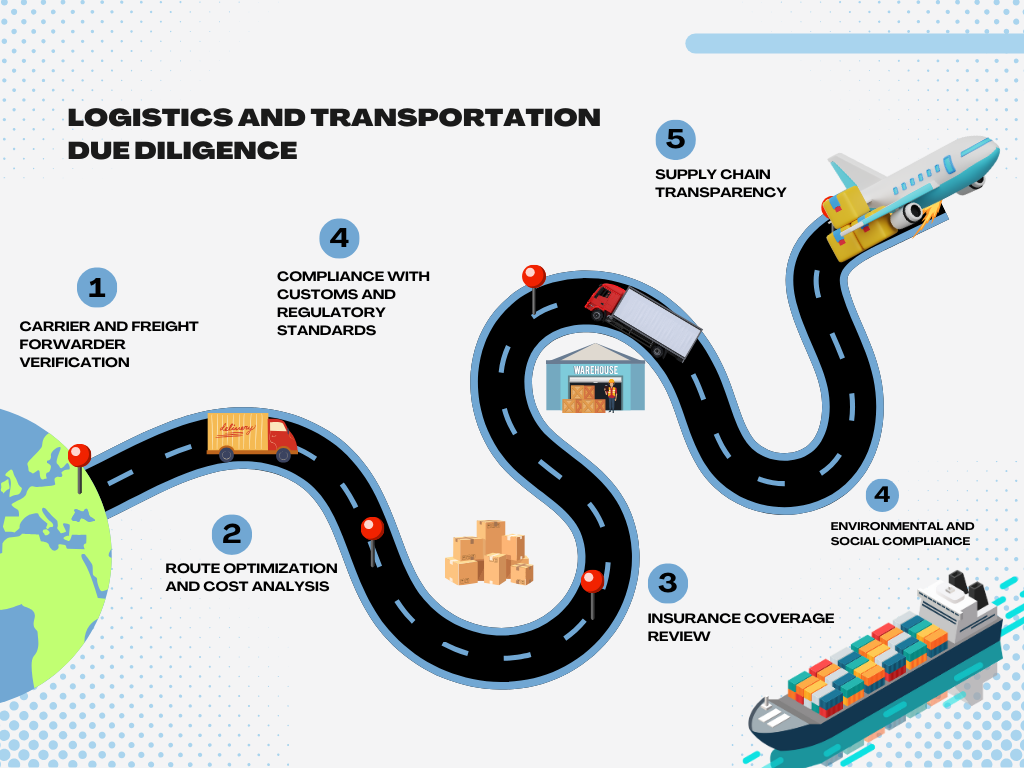
Logistics and Transportation Due Diligence is crucial in the buyer and supplier verification process for international trade, ensuring that goods are delivered on time, safely, and at the agreed-upon quality standards.
- Carrier Reliability and Reputation
- Transport Insurance Coverage
- Mode of Transport Selection
- Customs and Import/Export Compliance
- Packaging and Handling Standards
- Route and Transit Time Verification
- Contingency Planning and Risk Management
- Tracking and Visibility Technology
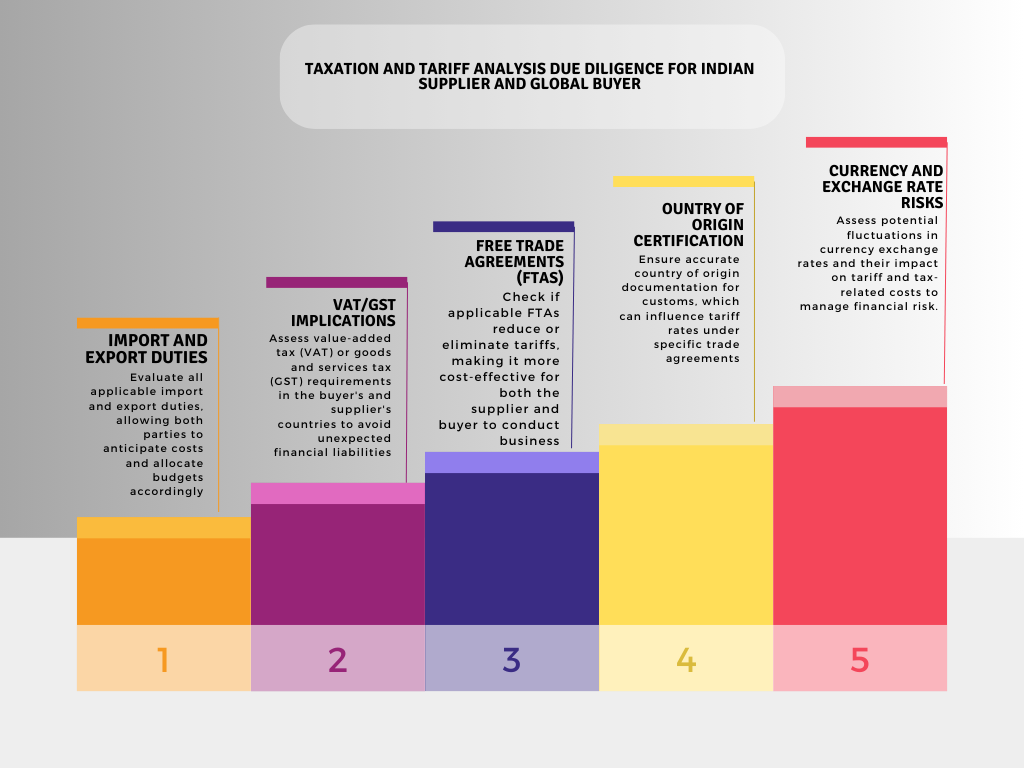
Taxation and Tariff Analysis
Taxation and Tariff Analysis Due Diligence is essential in the buyer and supplier verification process to identify and manage tax implications, import/export duties, and compliance with trade agreements.
- Tariff Classification Verification
- Import and Export Duties Assessment
- Free Trade Agreements (FTAs)
- Value-Added Tax (VAT) and GST Compliance
- Customs Documentation and Compliance
- Transfer Pricing Agreements
- Tax Residency and Withholding Tax Requirements
- Currency Exchange Impact on Tax Liabilities
Environmental and Social Due Diligence

Environmental and Social Due Diligence in buyer and supplier verification ensures that international trade partnerships align with environmental regulations and social responsibility standards.
- Environmental Compliance Verification
- Labor and Human Rights Standards
- Supply Chain Transparency
- Sustainable Resource Sourcing
- Waste Management and Recycling Practices
- Carbon Footprint Assessment
- Community Impact and Engagement
- Health and Safety Standards
Sanctions and Embargo Checks

Sanctions and Embargo Checks Due Diligence is essential in verifying buyers and suppliers in international trade to avoid engaging with entities or individuals restricted by international laws. This due diligence minimizes legal risks and ensures compliance with global trade regulations.
- Screening Against Sanctions Lists
- Embargoed Countries Verification
- Dual-Use Goods Assessment
- Beneficial Ownership Analysis
- Political Exposure Checks
- End-Use and End-User Verification
- Restricted Trade Zones Monitoring
- Continuous Monitoring and Updates
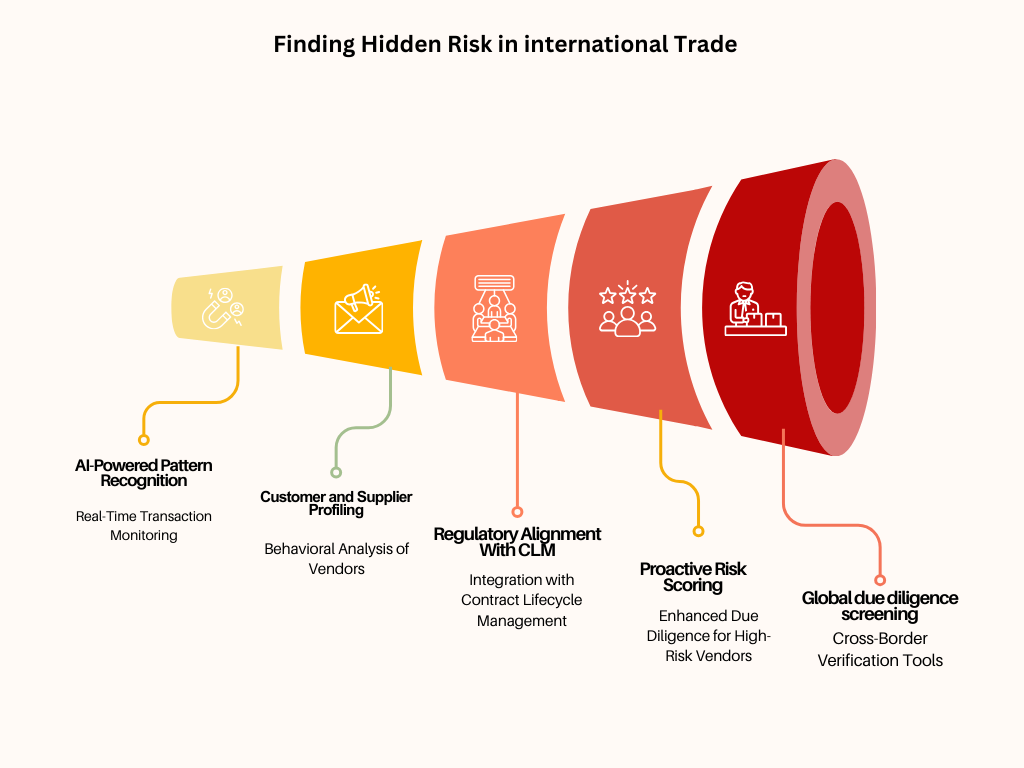
Implementing Buyer Market Fraud in International Trade
Buyer Market Fraud in International Trade involves deceptive practices where buyers exploit their stronger market position to defraud suppliers. Common tactics include manipulating payment terms, falsifying information about their purchasing capacity, or creating false claims of defective goods to demand unjustified discounts or refunds. In some cases, fraudulent buyers may place large orders with no intention of payment, or they may use fake identities and untraceable bank accounts. This type of fraud undermines supplier trust, incurs financial losses, and can damage long-term international trade relationships..


Supplier Market Fraud in International Trade
Supplier Market Fraud in International Trade refers to deceptive practices by suppliers aimed at exploiting buyers in the global marketplace. This type of fraud can manifest in various forms, including misrepresentation of product quality, delayed shipments, or providing counterfeit goods. Suppliers may also engage in tactics such as overcharging for products or services, submitting false invoices, or failing to adhere to contractual terms. Such fraudulent activities undermine trust in international trade, lead to significant financial losses for buyers, and disrupt supply chains. To mitigate the impact of supplier market fraud, businesses must implement rigorous verification processes, enforce strict quality control measures, and establish clear contractual agreements to protect their interests.
Supported By